Cloud computing has changed how businesses operate, and at the center of this transformation is Amazon Web Services, or AWS. What is AWS? Simply put, it’s the world’s most popular cloud platform that lets companies rent computing power instead of buying expensive servers. Today, AWS holds 31% of the global cloud market, serving millions of customers from startups to Fortune 500 companies.
The platform processes over 190 million requests per second, powering everything from Netflix streams to NASA space missions. Whether you’re running a small website or managing massive data operations, AWS provides the tools to make it happen. This guide will walk you through what AWS is, how it works, why businesses choose it, and how you can start using it today.
What Is Cloud Computing?
Before understanding AWS, you need to know what cloud computing means. Think of it as renting a computer that lives somewhere else, accessed through the internet. Instead of buying physical machines, you use resources stored in large data centers.
Cloud computing removes the need for companies to maintain their own servers. You can access files, run programs, and store data without owning any hardware. This approach saves money because you only pay for what you actually use.
The cloud offers three main types: public clouds (shared resources), private clouds (dedicated resources), and hybrid clouds (combination of both). AWS operates as a public cloud, meaning many customers share the same infrastructure.
Businesses prefer cloud computing because it’s flexible. You can increase capacity during busy times and reduce it when things slow down. This flexibility helps companies respond quickly to changing needs without wasting money.
What Is AWS?
AWS stands for Amazon Web Services, the cloud computing arm of Amazon that launched publicly in 2006. It provides on-demand computing resources including servers, storage, databases, networking, and software tools. Companies use AWS to build and run applications without managing physical infrastructure.
The platform offers over 200 different services covering almost every computing need imaginable. From hosting simple websites to training artificial intelligence models, AWS handles it all. These services work together like building blocks, letting you create custom solutions.
AWS operates on a pay-as-you-go model, meaning you’re charged based on actual usage rather than flat fees. This pricing structure makes it affordable for both small startups and large enterprises. You can start small and grow as your needs increase.
Amazon built AWS using the same infrastructure that powers its massive e-commerce operation. This means you’re using technology proven to handle millions of transactions every day. The reliability and scale that Amazon requires for itself now benefits all AWS customers.
Why AWS Is Important
AWS democratized access to enterprise-level technology that was once available only to large corporations. Now, a college student can launch a startup using the same infrastructure as major companies. This levels the playing field for innovation.
The platform accelerates how quickly businesses can launch new products and services. What used to take months of hardware procurement now happens in minutes. This speed gives companies a competitive advantage in fast-moving markets.
AWS eliminates huge upfront investments in technology infrastructure. Instead of spending millions on data centers, companies can start with just a credit card. This lower barrier to entry enables more people to test business ideas.
The service provides global reach instantly. With data centers on every continent, you can serve customers worldwide without building international offices. This global presence helps businesses expand into new markets quickly.
History Of Amazon Web Services (AWS)
2002 – AWS Services Launched: Amazon started offering its internal infrastructure as services to external developers. This marked the beginning of what would become the cloud computing revolution we know today.
2006 – Cloud Products Launched: AWS officially launched three core services: Simple Storage Service (S3), Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), and Simple Queue Service (SQS). These foundational products, particularly AWS storage services like S3, established the modern cloud computing model and provided scalable, reliable solutions for storing massive amounts of data.
2012 – First Customer Event: AWS held its first Re:Invent conference in Las Vegas with 6,000 attendees. This event became the annual gathering place for the AWS community.
2015 – Revenue Reached $4.6B: AWS crossed $4.6 billion in annual revenue, proving that cloud computing was becoming a mainstream business model. The profitability demonstrated the viability of the platform.
2016 – Surpassed $10B Revenue: Revenue doubled to over $10 billion, making AWS one of the fastest-growing enterprise technology services in history. This growth validated Amazon’s cloud strategy.
2016 – AWS Snowball, Snowmobile: Amazon introduced physical data transfer devices for customers moving massive amounts of data to the cloud. Snowmobile, a literal truck full of storage, could transfer 100 petabytes.
2019 – 100 Cloud Services Released: AWS announced over 100 new services and features in a single year, showing the rapid pace of innovation on the platform.
How Does AWS Work?
AWS functions through a network of services and infrastructure that work together to deliver computing power over the internet. Understanding how these components connect helps you make better decisions about using the platform.
1. Cloud Computing Foundation
- Run Applications Over Internet: AWS lets you run software programs through a web browser without installing anything locally. Your applications live in Amazon’s data centers, accessed from anywhere with internet connectivity.
- No Need For Physical Servers: You don’t buy, maintain, or upgrade hardware when using AWS. Amazon handles all the physical equipment, including repairs, cooling, and power management.
- Pay Only For Used Resources: Billing happens by the hour or second for most services. If you run a server for three hours, you pay for three hours. When you shut it down, the charges stop.
- Access Computing Resources Anytime: AWS services are available 24/7 from any location. You can create new servers, databases, or storage at 3 AM on a Sunday without waiting for anyone.
- Scale Resources Up Or Down: During busy periods, add more computing power instantly. When traffic decreases, reduce resources to save money. This flexibility happens in real-time.
- Use Virtual Machines Instead Of Hardware: Virtual servers act like physical computers but exist as software. One physical machine can host multiple virtual servers, making better use of hardware.
- Host Websites And Apps Easily: Deploy your website or application to AWS with a few clicks. The platform handles the technical details of making your site available to the world.
- Process Large Amounts Of Data: AWS provides the computing power to analyze massive datasets quickly. Tasks that would take days on a regular computer finish in hours.
2. Global Data Centers & Regions
- Multiple Data Centers Worldwide: AWS operates facilities across 33 geographic regions with 105 availability zones. Each region contains multiple separate data centers for redundancy.
- Reduced Latency For Users: Place your applications close to your customers to minimize delays. A user in Tokyo gets faster responses from servers in Tokyo than from servers in New York.
- Redundant Infrastructure Prevents Downtime: Each availability zone has independent power, cooling, and networking. If one zone fails, others continue operating without interruption.
- High Availability Across Regions: Spread your application across multiple regions for maximum reliability. Natural disasters or regional outages won’t affect your entire operation.
- Choose Closest Region To Users: Select where your data lives based on your customer locations. This improves performance and can help comply with data residency regulations.
- Disaster Recovery Made Easy: Back up your data to different geographic locations automatically as part of AWS disaster recovery. If something goes wrong in one place, you can restore operations quickly from another region.
- Replicate Data Across Locations: Copy information to multiple data centers simultaneously. This ensures your data remains accessible even during localized problems.
3. Core Compute Services
- Launch Virtual Servers (EC2): Elastic Compute Cloud creates virtual computers in minutes. These machines run just like physical servers but exist entirely as software.
- Select Server Size And Type: Choose from dozens of configurations optimized for different workloads. Pick more memory for databases or more processing power for calculations.
- Run Applications And Scripts: Install any software or run any code on your EC2 instances. You have full control over the operating system and installed programs.
- Handle Spikes In Traffic: Auto-scaling automatically adds servers when traffic increases and removes them when it decreases. Your application stays responsive without manual intervention.
- Automate Server Deployment: Use templates to create identical server configurations repeatedly. This automation ensures consistency and saves time when expanding your infrastructure.
- Load Balancing For Reliability: Distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers automatically. If one server fails, traffic redirects to healthy servers without users noticing.
- Flexible Operating System Options: Run Linux, Windows, or specialized operating systems. AWS supports various versions and distributions to match your requirements.
4. Cloud Storage & Databases
- Store Files Securely (S3): Simple Storage Service holds any type of file with 99.999999999% durability. Your data remains safe even if multiple storage devices fail.
- Structured And Unstructured Databases: AWS offers databases for organized data in tables and flexible storage for documents, images, and videos. Choose the right tool for your data type.
- Relational Databases (RDS): Managed database service supports MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and SQL Server. AWS handles backups, patches, and scaling automatically.
- NoSQL Databases (DynamoDB): Store data that doesn’t fit traditional table structures. DynamoDB handles massive scale with single-digit millisecond response times.
- Backup And Restore Data Easily: Schedule automatic backups of your databases and storage. Restore previous versions with a few clicks when needed.
- High Durability And Availability: Data replicates across multiple devices and facilities automatically. The chance of losing your information is extremely small.
- Access Data From Anywhere: Retrieve your files from any location with internet access. Share data between applications or with team members securely.
- Large-Scale Storage Without Hardware: Store petabytes of data without buying storage arrays or managing disks. AWS handles all hardware maintenance and upgrades.
5. Networking & Security Controls
- Virtual Private Clouds (VPC): Create isolated network environments within AWS. When implementing AWS security, a VPC acts like having your own private section of Amazon’s network infrastructure, helping isolate resources and limit exposure.
- Secure Network Connections: Establish encrypted tunnels between your office and AWS. Data travels securely over the internet or through dedicated connections.
- Firewalls For Protection: Configure security groups that act as virtual firewalls around your resources. Control which traffic can reach your servers and databases.
- Encrypt Sensitive Data: Protect information at rest and in transit using industry-standard encryption. AWS provides tools to manage encryption keys securely.
- Control User Permissions: Define exactly what each person or application can access. Grant minimum necessary permissions to reduce security risks.
- Identity And Access Management (IAM): Create user accounts, assign permissions, and track activities. IAM provides detailed control over who can do what in your AWS account.
- Protect Against Cyber Threats: AWS Shield guards against DDoS attacks automatically. Additional security services detect and respond to suspicious activities.
- Monitor Network Traffic: Track all network communications in real-time. Analyze traffic patterns to identify potential security issues before they become problems.
6. Managed Services & Tools
- Analytics Tools For Insights: Process and analyze data using services like AWS Athena and Redshift. Turn raw information into actionable business intelligence without building infrastructure.
- Machine Learning Capabilities: Build, train, and deploy AI models using SageMaker. Pre-built AI services recognize images, translate languages, and analyze text.
- Automation Of Routine Tasks: Lambda runs code automatically in response to events. Automate backups, processing tasks, and maintenance without managing servers.
- Monitoring And Logging Services: CloudWatch tracks performance metrics and application logs. Set alarms to notify you when something needs attention.
- Application Integration Services: Connect different applications and services together seamlessly. Pass data between systems without building custom integration code.
- DevOps Support For Deployment: Tools like CodePipeline and CodeDeploy automate software releases. Deploy new features faster with less risk of errors.
- Simplify Infrastructure Management: Managed services handle patching, backups, and scaling automatically. Focus on building applications instead of maintaining infrastructure.
- Build Scalable Applications Easily: Use serverless architectures where AWS manages all the underlying infrastructure. Your application scales automatically based on demand.
7. Pay-As-You-Go Pricing
- Only Pay For Usage: Charges calculate based on actual consumption measured by the second or hour. Stop using a service and the billing stops immediately.
- No Upfront Hardware Costs: Start using AWS with just a credit card and an email address. No capital expenditure required to begin your cloud journey.
- Reduce Unnecessary Spending: Turn off resources when not needed, like development servers overnight. This granular control helps optimize your costs.
- Flexible Monthly Billing: Review detailed invoices showing exactly what you used. Adjust your spending by changing which services and features you consume.
- Scale Resources Without Overspending: Add capacity during peak times and reduce it during slow periods. Pay more only when you need more resources.
- Cost-Effective For Small Businesses: Small companies access the same technology as large enterprises. The pay-as-you-go model means you never pay for unused capacity.
- Ideal For Startups And Enterprises: Whether you’re testing an idea or running global operations, AWS pricing scales with your needs. Both tiny and huge workloads benefit from the same pricing structure.
Advantages Of AWS
1. Scalability: AWS grows with your business seamlessly. Add or remove resources in minutes without long-term commitments. This flexibility means you’re never stuck with too much or too little capacity, adapting instantly to changing demands.
2. Reliability: Amazon guarantees 99.99% uptime for most services with redundant infrastructure across multiple locations. Your applications stay available even during hardware failures. This reliability comes from years of operational experience managing massive scale.
3. Cost-Efficiency: Eliminate capital expenses for hardware and reduce operational costs through automation. The pay-as-you-go model means startups can access enterprise technology without enterprise budgets. Many customers report 30-50% cost savings compared to traditional infrastructure.
4. Global Reach: Deploy applications in multiple continents within minutes without building international data centers. Serve customers faster by placing resources geographically close to them. This global infrastructure would cost billions for most companies to build themselves.
5. Security: AWS meets compliance requirements for regulated industries including healthcare, finance, and government. Multiple layers of security protect your data and applications. Amazon invests heavily in security because their own business depends on it.
6. Wide Range Of Services: Over 200 services cover computing, storage, databases, machine learning, IoT, and more. This breadth means you can build almost anything without leaving the AWS ecosystem. New services launch regularly, expanding capabilities continuously.
Disadvantages Of AWS
1. Complex Pricing: Understanding costs requires careful planning with hundreds of pricing variables to consider. Bills can surprise you if you don’t monitor usage closely. The complexity sometimes makes it hard to predict monthly expenses accurately.
2. Steep Learning Curve: AWS offers so many services that beginners feel overwhelmed about where to start. Becoming proficient requires significant time investment and often certification courses. The complexity means you might need specialized staff or consultants.
3. Dependency On Internet: Everything requires reliable internet connectivity to function properly. If your connection fails, you can’t access your applications or data. This dependency creates vulnerability for businesses with poor connectivity.
4. Limited Control Over Hardware: You can’t physically access the servers running your applications or customize hardware configurations. Some specialized workloads require specific hardware that AWS might not offer. This limitation affects organizations with unique technical requirements.
Top Applications For AWS
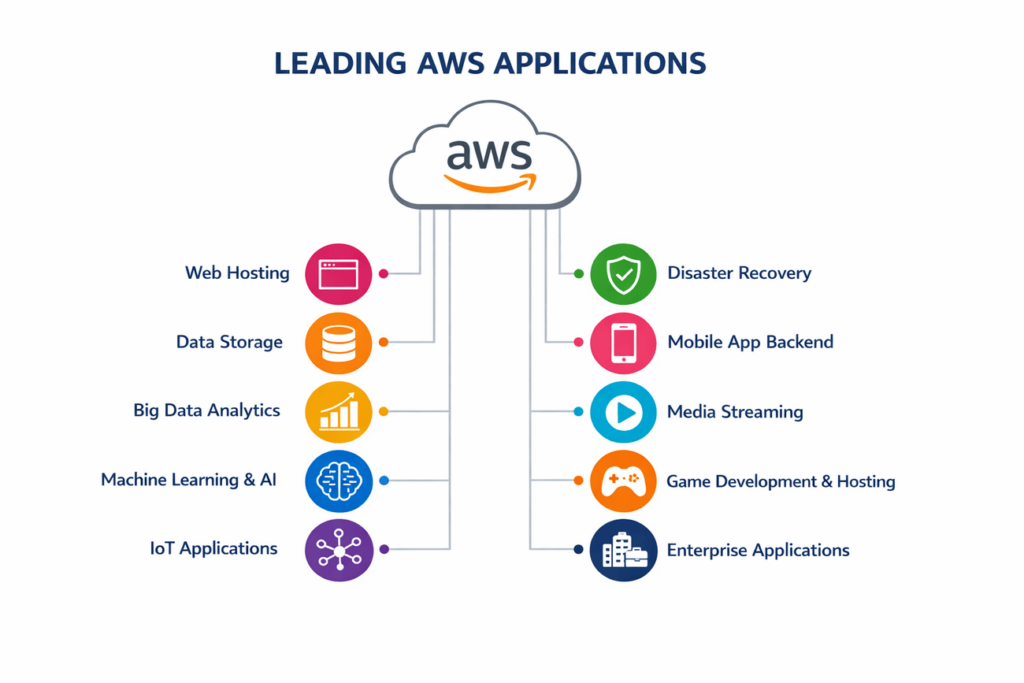
1. Web Hosting: Companies host websites and web applications on EC2 and S3, handling everything from small blogs to high-traffic sites. AWS provides the reliability and scale needed for modern web properties.
2. Data Storage: Organizations use S3 for backups, archives, and content distribution. The low cost and high durability make it ideal for long-term storage needs without worrying about hardware failures.
3. Big Data Analytics: Businesses analyze massive datasets using Redshift, EMR, and Athena. These tools process terabytes of information to find patterns and insights that drive decision-making.
4. Machine Learning & AI: Companies build recommendation engines, chatbots, and predictive models using SageMaker. Pre-trained AI services add intelligence to applications without requiring data science expertise.
5. IoT Applications: Connected devices send data to AWS IoT services for processing and analysis. Smart homes, industrial sensors, and wearable devices use AWS as their backend infrastructure.
6. Disaster Recovery: Organizations replicate critical systems to AWS for business continuity. Planning these moves often involves understanding the AWS migration phases to ensure a smooth transition. In case of primary site failure, operations continue running on AWS until normal operations resume.
7. Mobile Application Backend: Mobile apps use AWS as their server infrastructure for user authentication, data storage, and push notifications. This backend scales automatically as apps gain users.
8. Media Streaming: Video and audio content streams from AWS to millions of viewers simultaneously. Services like Netflix rely on AWS for their entire streaming infrastructure.
9. Game Development & Hosting: Game studios use AWS for multiplayer servers, player data storage, and game analytics. The global infrastructure ensures players worldwide get low-latency experiences.
10. Enterprise Applications: Companies run ERP, CRM, and other business applications on AWS. This cloud deployment reduces IT overhead while maintaining enterprise-grade performance.
AWS Vs Other Cloud Solutions
| Feature | AWS | Microsoft Azure | Google Cloud | IBM Cloud | Oracle Cloud | Alibaba Cloud | DigitalOcean |
| Market Share | 32% | 23% | 10% | 4% | 2% | 4% | <1% |
| Launch Year | 2006 | 2010 | 2008 | 2013 | 2016 | 2009 | 2011 |
| Global Regions | 33 | 60+ | 40+ | 19 | 44 | 27 | 15 |
| Service Count | 200+ | 200+ | 150+ | 170+ | 100+ | 120+ | 50+ |
| Pricing Model | Pay-as-you-go, Reserved, Spot | Pay-as-you-go, Reserved, Hybrid | Pay-as-you-go, Committed | Pay-as-you-go, Reserved | Pay-as-you-go, Universal Credits | Pay-as-you-go, Subscription | Simple hourly/monthly |
| Free Tier | 12 months + always free services | 12 months + always free | 90 days + always free | Limited free tier | Limited free tier | Limited free tier | $200 credit |
| Compute Services | EC2, Lambda, Fargate | Virtual Machines, Functions | Compute Engine, Cloud Run | Virtual Servers, Functions | Compute, Functions | ECS, Function Compute | Droplets, App Platform |
| Storage | S3, EBS, Glacier | Blob Storage, Files | Cloud Storage, Persistent Disk | Object Storage, Block | Object Storage, Block | OSS, Block Storage | Spaces, Volumes |
| Database Options | RDS, DynamoDB, Aurora | SQL Database, Cosmos DB | Cloud SQL, Firestore | Db2, Cloudant | Autonomous Database, MySQL | ApsaraDB, PolarDB | Managed Databases |
| Machine Learning | SageMaker, extensive AI services | Azure ML, Cognitive Services | Vertex AI, AI Platform | Watson Studio | AI Services | Machine Learning Platform | Limited |
| Enterprise Integration | Strong across all sectors | Excellent with Microsoft ecosystem | Strong in data analytics | Strong in enterprise legacy | Excellent with Oracle products | Strong in Asia-Pacific | Focused on developers |
| Best For | General purpose, broadest services | Microsoft shops, hybrid cloud | Data analytics, Kubernetes | Enterprise, mainframe integration | Database-heavy workloads | Asian markets | Developers, simple deployments |
| Certification Programs | Extensive (Foundational to Specialty) | Extensive (Fundamentals to Expert) | Comprehensive (Associate to Professional) | Multiple levels available | Multiple levels available | Multiple levels available | Limited |
| Support Plans | 4 tiers (Developer to Enterprise) | 5 tiers (Developer to Premier) | 4 tiers (Basic to Enterprise) | Multiple support options | Multiple support tiers | Multiple support options | Community, Business, Enterprise |
| Unique Strengths | First-mover, largest ecosystem | Hybrid capabilities, Active Directory | Big data tools, Kubernetes expertise | Mainframe integration, enterprise AI | Database performance, autonomous features | Strong in China, cost-effective | Simple pricing, developer-friendly |
| Primary Limitations | Complex pricing, steep learning | Confusing service names, limited regions vs AWS | Smaller service catalog | Smaller market presence | Limited third-party integrations | Limited presence outside Asia | Limited enterprise features |
10 Major Companies Running On AWS
Netflix: The streaming giant uses AWS to deliver content to over 200 million subscribers worldwide. Netflix runs its entire streaming infrastructure on AWS, relying on the platform’s scale and reliability for smooth video delivery.
Airbnb: The hospitality platform hosts its website and mobile apps on AWS, handling millions of bookings daily. AWS’s scalability helps Airbnb manage huge traffic spikes during peak booking seasons without performance issues.
Spotify: The music streaming service stores and delivers songs to 500+ million users through AWS infrastructure. This partnership allows Spotify to focus on user experience rather than managing servers and data centers.
Adobe: Creative Cloud applications and services run on AWS, serving millions of creative professionals globally. AWS provides the computing power needed for resource-intensive tasks like video rendering and image processing.
LinkedIn: The professional networking platform migrated significant portions of its infrastructure to AWS for better scalability. Using AWS migration tools, this move helps LinkedIn handle variable traffic patterns as professionals access the platform throughout the workday.
Samsung: The technology giant uses AWS for SmartThings, its IoT platform connecting smart home devices. AWS handles the massive scale of data from millions of connected devices sending information continuously.
NASA: The space agency uses AWS for various missions including Mars rover image processing and space exploration data analysis. AWS provides the computing power needed for complex scientific calculations and data storage.
General Electric (GE): The industrial conglomerate runs its Predix IoT platform on AWS, connecting industrial equipment worldwide. This infrastructure processes sensor data from aircraft engines, wind turbines, and manufacturing equipment.
Slack: The business communication platform relies on AWS for messaging infrastructure serving millions of daily active users. AWS’s reliability ensures teams can communicate without interruption.
Pinterest: The visual discovery platform uses AWS to store billions of pins and deliver personalized content to users. AWS’s machine learning services help Pinterest improve content recommendations continuously.
How To Get Started With AWS
To understand AWS effectively, it helps to start with the basics. These steps will guide you through setting up an account, exploring core services, and learning key concepts so you can confidently navigate the AWS cloud.
1. Create An AWS Account
Visit the AWS website and sign up using your email address and payment information. The registration process takes just a few minutes and requires a credit card for identity verification even with the free tier.
2. Understand The Free Tier
AWS offers 12 months of free access to many services with usage limits. Learn these limits to experiment without charges. Some services like Lambda offer permanent free tier benefits.
3. Familiarize With AWS Console
The web-based management console provides access to all services. Spend time exploring the interface to understand how different sections organize services and features available to you.
4. Explore Core Services
Start with foundational services like EC2, S3, and RDS. Watch tutorials and follow documentation to launch your first virtual server or create storage buckets for practicing basic operations.
5. Set Up IAM Users & Permissions
Never use your root account for daily work. Create IAM users with specific permissions for different tasks. This security practice protects your account from accidental or malicious damage.
6. Launch A Virtual Server
Use EC2 to create your first virtual machine, choosing a free tier eligible instance type. Connect to it and install software to understand how cloud servers work differently from physical machines.
7. Upload And Manage Data
Create an S3 bucket and upload files to understand object storage. Configure permissions to control who can access your data and experiment with different storage classes.
8. Monitor Resources
Set up CloudWatch to track your resource usage and costs. Create billing alarms to notify you if charges exceed expected amounts, preventing surprise bills as you learn.
9. Learn Security Best Practices
Enable multi-factor authentication, use strong passwords, and encrypt sensitive data. Understanding security fundamentals prevents costly mistakes and protects your applications from threats.
10. Explore Advanced Services
After mastering basics, experiment with databases, serverless functions, and machine learning services. You can also try AWS DevOps tools like CodePipeline and CodeDeploy to automate deployment and manage infrastructure efficiently. AWS provides extensive documentation and training resources to expand your knowledge progressively.
How AWS Pricing Works
Pay-As-You-Go: Standard pricing charges based on actual usage without upfront commitments. You’re billed for compute time by the second, data storage by the gigabyte, and data transfer by volume consumed.
Free Tier: New accounts receive 12 months of limited free usage across many services. This allows you to experiment and learn without costs. Some services offer permanent free tier allowances even after 12 months.
Reserved Instances: Commit to using specific resources for one or three years and receive up to 75% discounts. This option benefits predictable workloads where you know you’ll need resources long-term.
Spot Instances: Bid on unused EC2 capacity at up to 90% discounts compared to on-demand prices. These instances can be interrupted with two-minute notice, making them suitable for flexible, fault-tolerant workloads.
Savings Plans: Flexible pricing model where you commit to a certain dollar amount per hour for one or three years. This provides similar discounts to reserved instances but with more flexibility across instance types.
Tiered Pricing: Many services offer volume discounts where per-unit costs decrease as usage increases. This benefits large-scale operations and encourages consolidating workloads on AWS.
No Upfront Costs: Start using services immediately without capital investment in hardware or long-term contracts. This low barrier to entry helps startups and small businesses access enterprise technology.
Cost Management Tools: AWS Cost Explorer visualizes spending patterns and forecasts future costs. Budget alerts notify you when spending approaches defined limits, helping control expenses proactively.
FAQs
What Is Amazon Web Services (AWS)?
Amazon Web Services is a cloud computing platform that provides on-demand access to computing resources including servers, storage, databases, and software tools without requiring physical hardware ownership.
What Does AWS Stand For?
AWS stands for Amazon Web Services, the cloud computing division of Amazon that offers over 200 services to businesses and individuals worldwide.
What Is Amazon Web Services Used For?
Amazon Web Services is used for web hosting, data storage, application development, machine learning, big data analytics, disaster recovery, IoT applications, and running enterprise software in the cloud.
What Are The Pros Of AWS?
AWS offers scalability, reliability with 99.99% uptime, cost-efficiency through pay-as-you-go pricing, global infrastructure with 33 regions, strong security with compliance certifications, and over 200 services covering diverse use cases.
What Are The Cons Of AWS?
AWS has complex pricing that’s difficult to predict, a steep learning curve due to numerous services, complete dependency on internet connectivity, and limited control over physical hardware configurations.
Why Choose AWS Over Other Cloud Providers?
AWS provides the largest service catalog with 200+ offerings, most global regions, strongest ecosystem of partners, earliest market entry providing maturity, and proven scalability demonstrated by major companies like Netflix.
How Much Does AWS Cost?
AWS costs vary widely based on usage with pay-as-you-go pricing. Simple websites may cost $5-50 monthly while enterprise applications can reach thousands. The free tier offers 12 months of limited free access.
What Are The Main AWS Services I Should Know As A Beginner?
Beginners should focus on EC2 for virtual servers, S3 for storage, RDS for databases, VPC for networking, IAM for security, and Lambda for serverless computing as foundational services.
What Is AWS Cloud Computing?
AWS cloud computing means accessing computing resources over the internet from Amazon’s data centers instead of owning and managing physical servers, paying only for what you use.
Can I Host My Website On AWS?
Yes, AWS supports website hosting using services like EC2 for dynamic sites, S3 for static sites, or Lightsail for simplified WordPress hosting with various pricing options.
Do I Need Coding Knowledge To Use AWS?
Basic AWS usage requires minimal coding, but advanced implementations need programming skills in languages like Python or JavaScript. AWS provides visual tools for common tasks without coding.
How Does AWS Compare With Azure And Google Cloud?
AWS leads in market share at 32% with the most services and regions, Azure excels in Microsoft integration, while Google Cloud specializes in data analytics and Kubernetes expertise.
Conclusion
AWS has transformed how businesses approach technology infrastructure by making enterprise-grade computing resources accessible to everyone. From small startups to global corporations, millions of customers rely on AWS for reliability, scalability, and innovation. The platform’s pay-as-you-go pricing removes financial barriers while the breadth of services supports virtually any workload. Whether you’re building a simple website or processing massive datasets, AWS provides the tools and infrastructure needed to succeed. The learning curve might seem steep initially, but the investment pays off through reduced costs, improved agility, and access to cutting-edge technology. As cloud computing continues evolving, AWS remains at the forefront, constantly releasing new services and features that push technological boundaries.
Folio3 Cloud Services specializes in helping organizations maximize their AWS investments through expert cloud architecture, data engineering, and migration services. Our team designs scalable solutions leveraging AWS services like Redshift, EMR, and SageMaker to unlock the full potential of your data. Whether you’re planning your first cloud migration or optimizing existing infrastructure, Folio3’s certified AWS professionals provide the expertise needed to ensure successful implementation, cost optimization, and ongoing management of your AWS environment.